We see the effect of a change in demand on the equilibrium price, supply remaining constant. Let us now see what happens to the equilibrium position when there is a shift in the supply curve, demand remaining constant. The shifts in supply curve occur when there is an increase or decrease in supply caused by factors other than the price of the commodity.
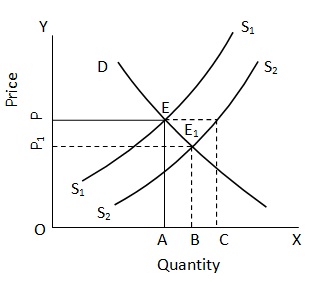
Here, DD and S1 S1 are the original demand and supply curves respectively. EA or OP is the equilibrium price and OA is the equilibrium quantity. An increase in supply of the product causes a shift in the supply curve towards the right. S2S2 is the new supply curve. If the price were to remain at OP, demand would be unchanged at OA but supply would increase to OC. Thus, there would be supply in excess of demand. This would result in a fall in price, alongwith which supply would also start falling. In this way, a new equilibrium position will emerge at E1, where price is E1 B or OP1 and the quantity demanded and supplied of the commodity are both equal at the new OB level. Thus, an increase in supply of a commodity causes a decrease in the equilibrium price and an increase in the quantity bought and sold at the equilibrium price and an increase in the quantity bought and sold at the equilibrium.
A decrease in supply will result in a leftward shift in the supply curve as a result of which the equilibrium price will rise and the equilibrium quantity will fall. In the above diagram, if supply were to fall from S2S2 to S1S1, the equilibrium price will rise from OP, to OP and the quantity demanded and supplied at the new equilibrium position will fall from OB to OA.
SUBMIT ASSIGNMENT NOW!