A decrease in aggregate supply means less output is supplied at any given price level than before and causes an upward (rightward) (leftward) shift in SRAS curve. An increase in supply shows that a larger amount than before is offered for sale at each given price level and this causes a downward (rightward) shift in the SRAS curve. The shows the effect of aggregate supply shocks on GDP and price level.
A decrease in aggregate supply causes an increase in price level and decline in real GDP. This situation where a rising price level is accompanied by a decrease in real national income (GDP) is called stagflation which is coined by joining two words,, viz., stagnation which means slow or even negative growth(falling national output) and inflation which denotes sustained rise in price level. This situation is shown where a decrease in aggregate supply shifts the SRAS0 to SRAS1. With given aggregate demand curve AD, the point of intersection or equilibrium position shifts E0 to E1. This result in fall in GDP form Y0 to Y1 and rise in price level from P0 to P1.
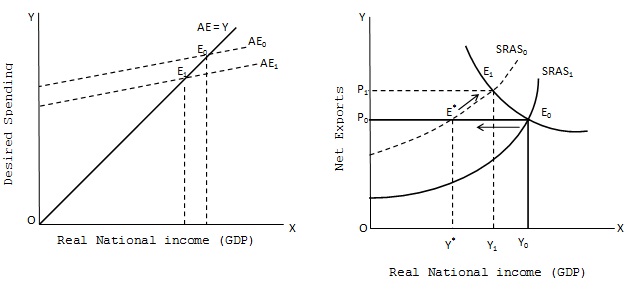
An increase in aggregate supply shifts the SRAS curve rightward (downward) from SRAS1 to SRAS0 and causes expansion in GDP from Y1 to Y0 and fall in price from P1 to P0.
Aggregate supply shocks cause the price level and real GDP to change in opposite directions; with an increase in supply the price level falls and output rises; with a decrease in supply the price level rises and output falls.
SUBMIT ASSIGNMENT NOW!